

File management refers to the ability to maintain computer files and folders in an organized manner so that information can be quickly filed or retrieved. I like to use the example of metal filing cabinets. What a mess these filing systems would be if people merely took papers and threw them into any folder or drawer in the filing cabinet. Instead, logical filing systems are set to make filing and retrieval an easy task. This should be the same with a computerized filing system. Think about the information you will be saving on your computer and then set up folders to store them so that you can find them when needed.
COMPONENTS OF COMPUTER STORAGE
Level 1: Disk Drives
When saving or opening files, the first thing the computer needs to know is the disk drive where the file is located. Below are the most common disk drives and their respective drive letters. Check your own system to see what drives and drive letters are being used by your computer.
A: the first floppy disk drive (or removable storage device)
B: the second floppy disk drive (or removable storage device)
C: the hard drive (some hard drives have more than one drive letter due to "partitioning")
D: The CD-Rom drive
F - Z: normally reserved for the file server
Level 2: Folder(s)
Once the computer is at the correct disk drive, it will need to know what folder the file is stored in. Folders can be inside other folders (subfolders). The computer needs to know specifically all the levels of folders it must go through in order to find the file. Look at the examples below.
This image shows the different disk drives on the computer (drives A, C, and R). Which drive contains the file?
Here, the computer has been told to go to drive A. Now, which folder contains the file?
This image shows how each folder can contain subfolders. The computer must know all levels of folders it must go through in order to reach the file.
Level 3: Filename
Once you have indicated the correct disk drive and folder levels, the last step is to let the computer know the filename of the item you want. See the example below.
A path is journey the computer will take through all three levels in order to get to the file. What is the path to the file called wintitle2.gif (shown above)? Remember:
- What drive must the computer go to?
- What folder(s) must it go through?
- What filename is the computer looking for?Click HERE to see the correct answer.
MANAGING YOUR FILES
There are many ways to see what folders and files are on a disk. My favorite is by using the program called Windows Explorer. You can get to this program by clicking the START button, highlight PROGRAMS, find WINDOWS EXPLORER and click on it. Your screen will look similar to the following (the basic layout is the same although there will be different drives and folders depending on the machine you are using).
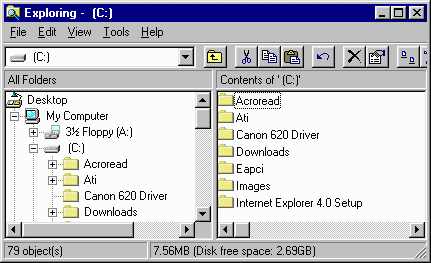
The left side of the window shows the drives and folders. A plus sign (+) next to a drive or folder indicates that there are more folders inside. Go into Windows Explorer on your machine and try clicking the + symbol to see the additional folders.
The right side of the window shows the contents of the highlighted item on the left. Click on a drive or folder to see its contents displayed in the right window pane.
*Note: There are several ways to do all of the tasks that are listed below. This tutorial will use the menu bar options only. |
Create a New Folder:
Select the drive or folder where you would like the new folder placed by clicking on it once.
Select the File menu, highlight New, then click on Folder.
A folder will appear with the words New Folder highlighted. Type the name of the folder and press the Enter key on the keyboard to finish the task.
Copy or Move Files:
Select the file you want to copy (or move) by clicking on it once.
*You can highlight several files at once by holding down the Control key while you click on the files.Select the Edit menu then the Copy option (select Cut if you are going to move the file).
Select (by clicking once) the drive or folder where you are copying or moving the file.
Click the Edit menu and then select the Paste option.
Click HERE to learn two different methods of copying or moving files.
How to Rename a File or Folder:
Highlight the file or folder to be renamed.
Select the File menu and the Rename option.
Type in the new name. Press Enter.
How to Delete a File or Folder:
Highlight the file or folder
Press the Delete key on the keyboard.
Say YES when asked if you really want to delete the file/folder.
When a file or folder is deleted from the hard drive, it is sent to the Recycle Bin. It will stay there until you empty it or until it gets too full and some of the older files get "pushed out".
How to Find a File:
In Windows Explorer, select the Tools menu, Find, Files or Folders
Be sure the Look In box inidicates the correct drive and/or folder.
In the Name box type in the file name you are looking for. If you don't remember the file name, type in a asterisk followed by a period and the file extension type. (For example: *.doc would find all files that end with .doc -- which are all Word files).
SAVING FILES
A common way to save a data file that you have created is to click the File menu and the Save As option. A popup window will appear (like the one below).
*NOTE: Filenames should never contain a period! Most programs will put a period and a 3 letter extension at the end of a filename to tag it as one of its own. |
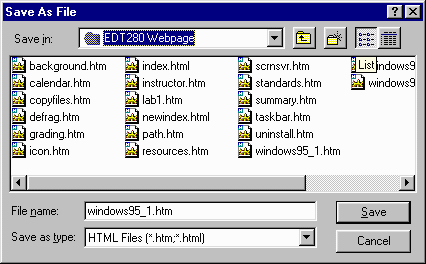 |
SHARED FOLDERS
If a school is on a network, a new method of having assignments submitted is to have a class shared folder on the file server. Students "drop" their files into this folder and the teacher can then "pick it up" when ready to grade. It works something like:
Students must first save their completed project to the hard drive, floppy drive, or some other location.
Next, it is necessary to use the Windows Explorer program to copy the file from the original saved location to the shared folder on the file server.
Students are given limited rights to this folder; usually only the ability to save a file. The ability to delete files or see other files in the folder is prohibited.
The teacher has full rights to the folder, giving him/her the ability to open files, enter comments, print the file, and resave it. Additionally, if there is a collaborative project underway, the teacher can merge several files together into one large group or class file.
| Class Calendar | Grading Method | Resources | Instructor | Tech Certification Standards |
Home |
This website developed and maintained by Dot Garman, Educational Technology Consultant
Last updated on 02-Jan-00
All rights reserved © 1999-2000